Tangent to the circle:
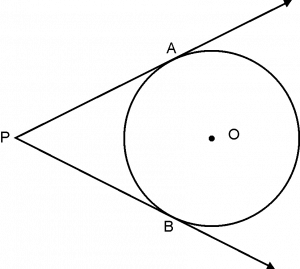
A line that intersects the circle at only one point is called a tangent.
* There is only one tangent at a point on the circle.
* There are two tangents to a circle from a point outside the circle.
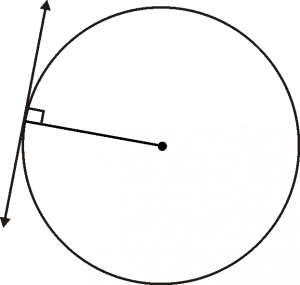
Length of tangent :
The length of tangent from the external point and point of contact with the circle is called the length of the tangent.
Theorem 1
The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contacts.
Given:
A circle with centre O .
Line PQ is tangent, touches the circle at P.
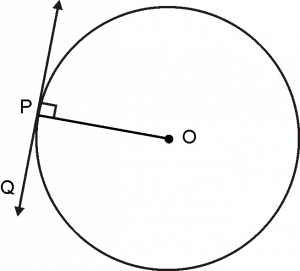
Proof
Theorem 2
Converse of the theorem:
Given a line which is perpendicular to radius at the end point of the radius then that line is tangent to the circle.
Given:
A circle with centre O .
To Prove
XY is tangent to the circle.

Proof
Take any point Q on XY . Q is appoint other than P.
So OQ is hypotenuse
We can say
Q is point outside the circle.
So all the points on line XY are outside the circle.
Only point P is on the circle.
Point of intersection of line and circle is only point P.
Line XY is tangent to the circle.
Theorem 3
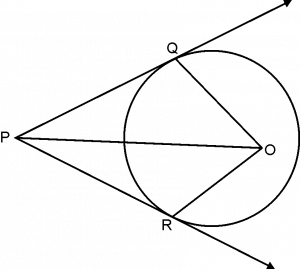
The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
Given:
O is centre of the circle.
PQ, PR are two tangents drawn from point .
To Prove
PQ = PR
Proof
…………………..(R.H.S)
PQ = PR ………….(CPCT)