
The fundamental law of electrostatics states that Like charges repel and unlike charges attract each other.
According to Coulomb’s law, the force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is
(i) directly proportional to the product of the two charges and
(ii) inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between them. Mathematically,
The value of K depends on the nature of the medium between the two charges and the system of unit chosen.
For charges in vacuum,.
It is the SI unit of charge. One coulomb is defined as that amount of charge which repels an equal and similar charge with a force of
when placed in vacuum at a distance of 1 metre from it.
The flow of electric charge is known as electric current. Electric current is carried by moving electrons through a conductor.
The electric current is defined as a flow of electric charges (called electrons) in a conductor such as a metal wire
When a cell or a battery is connected between the ends of the metal wire. Then an electric force acts on the electrons present in the wire, Since the electrons are negatively charged, the start moving from negative end to the positive end of the wire
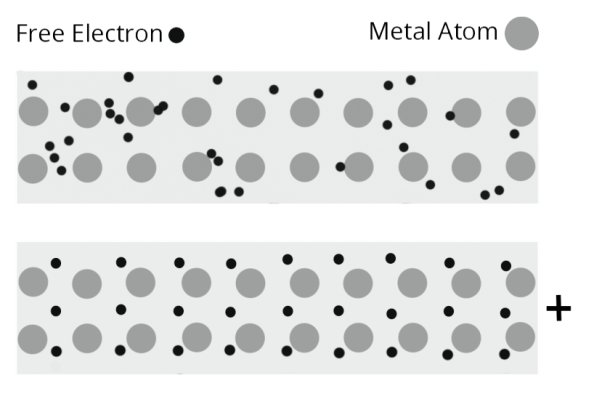
This flow of electrons constitutes the electric current in the wire.
Electric current can be expressed considering a net charge Q which flows across any cross-section of a conductor in time t. Then the current I, through the cross-section is I can be expressed as:
The SI unit of electric current is ampere.
AMPERE: One ampere isconstituted by the flow of one coulomb of charge per second through any cross-section of a conductor. That is,
or
An important property of electric charges is that:
(i) Opposite charges (or Unlike charges) attract each other.
(ii) Similar charges (or Like charges) repel each other.
Conductors:
Those substances through which electricity can flow are called conductors. The presence of “free electrons’ in a substance makes it a conductor (of electricity). All the metals like silver, copper and aluminium, etc.
Insulators:
Those substances through which electricity cannot flow are called insulators. Examples are glass, ebonite, rubber, most plastics, paper, dry wood, cotton, mica, Bakelite, porcelain and dry air.
Electricity can be classified into two parts:
(i) Static electricity, and
(ii) Current electricity.
(i)Static electricity: In static electricity, the electric charges remain at rest (or stationary), they do not move.
(ii)Current electricity: In current electricity, the electric charges are in motion.
For detailed notes on these topics download the Learning App.
The simplest way to maintain a potential difference between the two ends of a conductor so as to get a continuous flow of current is to connect the conductor between the terminals of a cell or a battery.