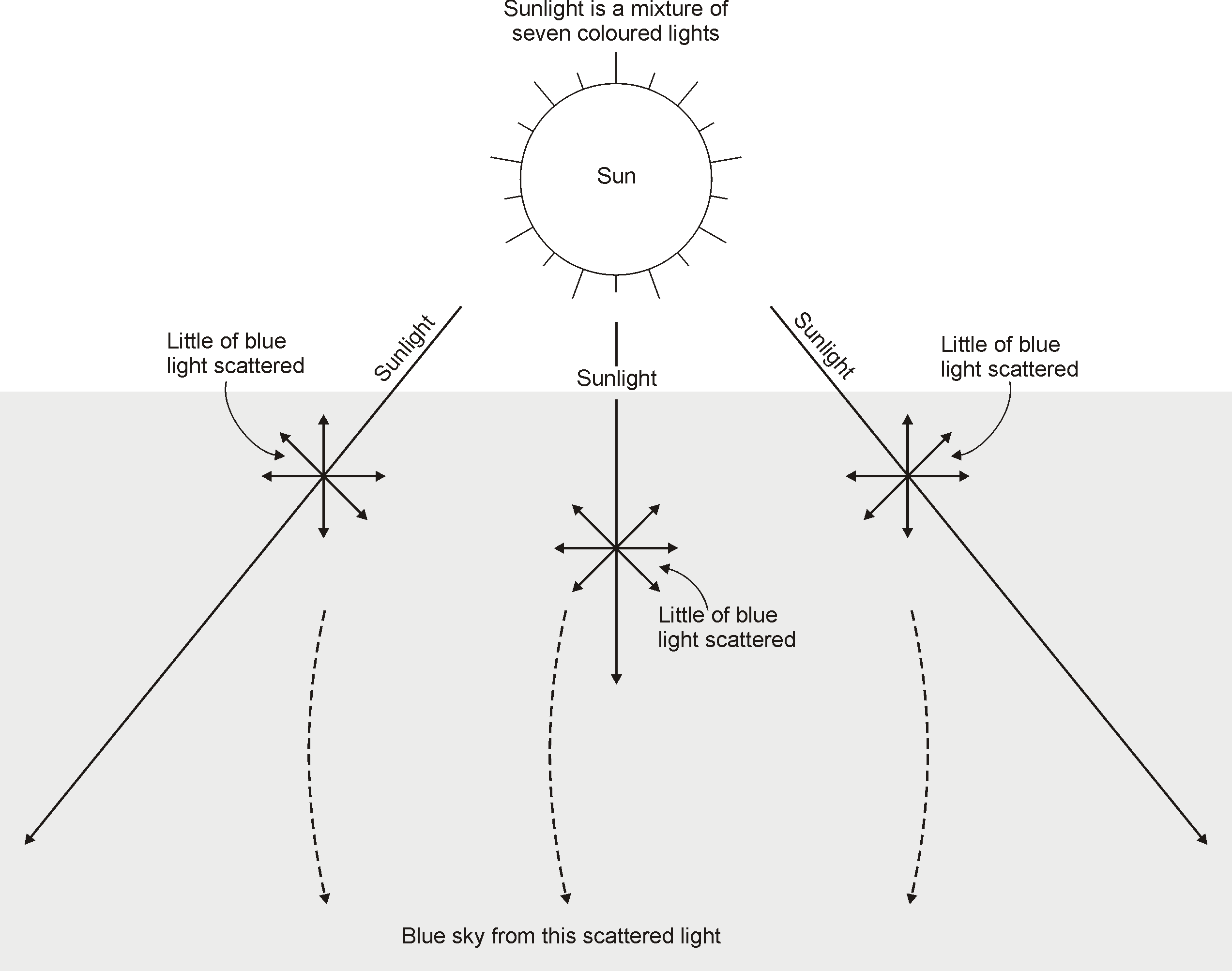
- The scattering of blue component of the white sunlight by air molecules present in the atmosphere causes the blue colour of the sky.
- The sunlight is made up of seven coloured lights mixed together.
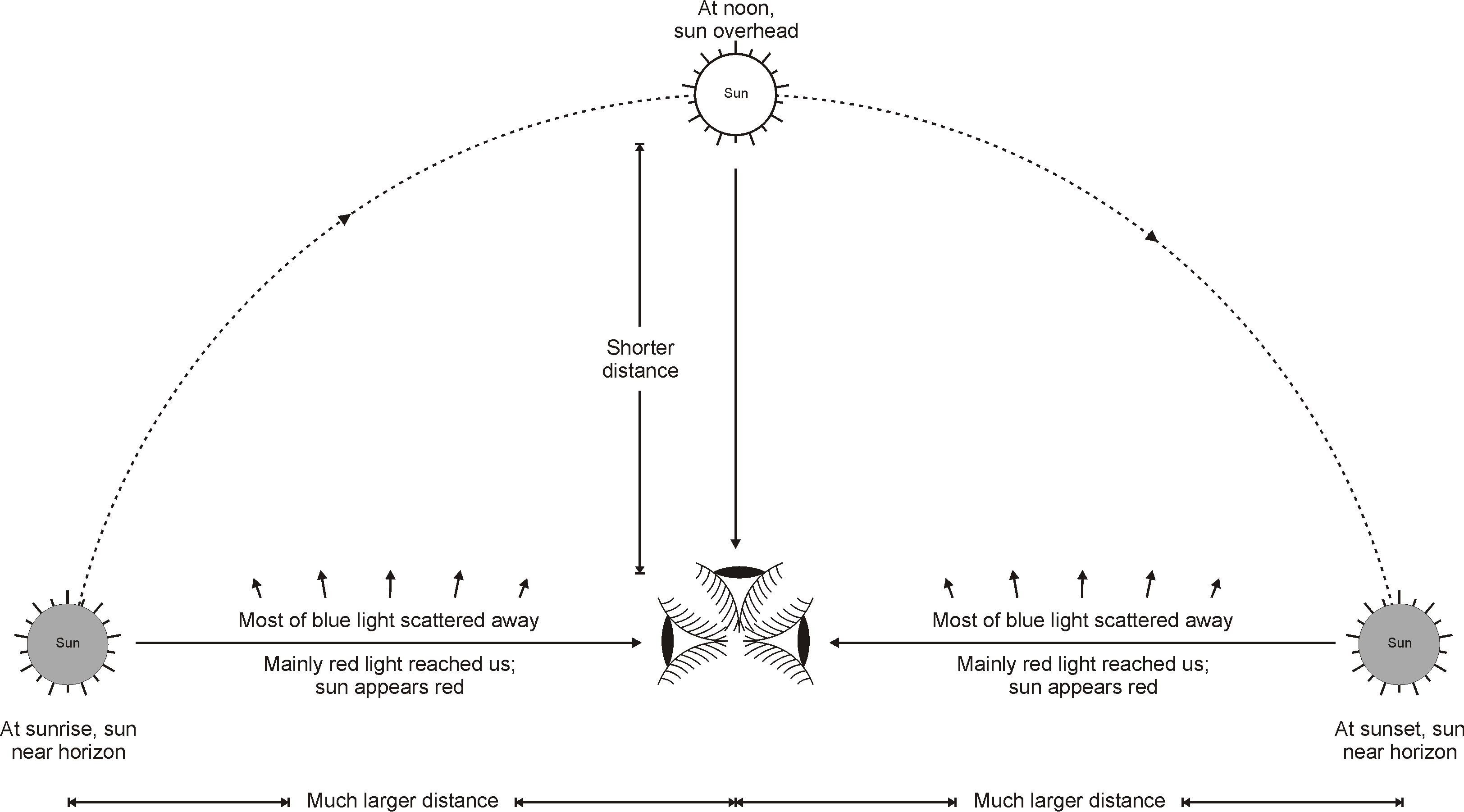
- The molecules of air and other fine particles in the atmosphere have size smaller than the wavelength of visible light. These are more effective in scattering light of shorter wavelengths at the blue end than light of longer wavelengths at the red end.
- The red light has a wavelength about 1.8 times greater than blue light. Thus, when sunlight passes through the atmosphere, the fine particles in air scatter the blue colour (shorter wavelengths) more strongly than red. The scattered blue light enters our eyes.
In outer space, the sky looks dark and black instead of blue: This is because there is not atmosphere containing air in the outer space to scatter sunlight. Scattering is not prominent at such heights.