
According to Ohm’s law, at constant temperature and physical conditions, the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends.
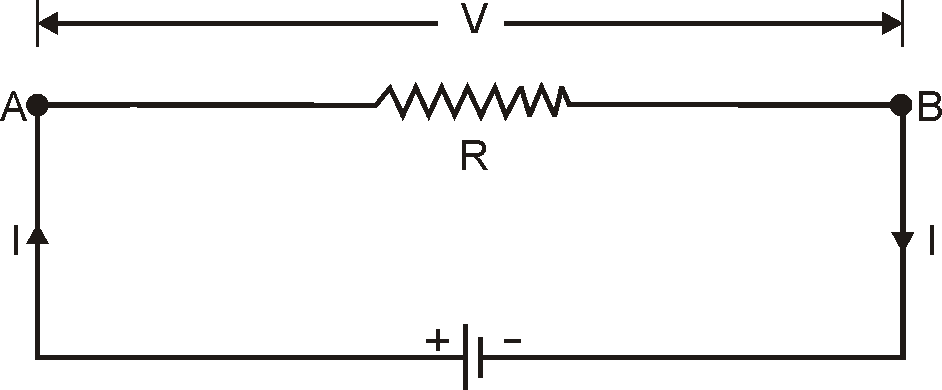
where, V is the potential difference measured across the conductor (in volts)
I is the current through the conductor (in amperes)
R is the constant of proportionality called resistance (in ohms)