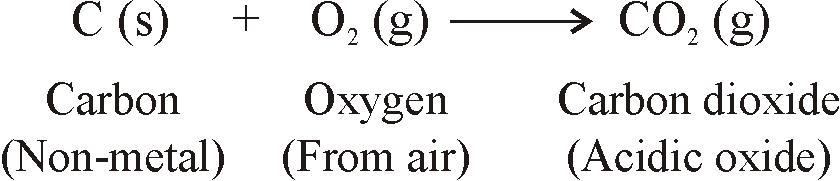REACTION OF NON METALS
REACTION OF NON-METALS WITH OXYGEN
- Non- metals react with oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides.
- For example: Carbon forms an acidic oxide CO2, sulphur forms an acidic oxide SO2, and hydrogen forms a neutral oxide, H2
- The non-metal oxides are covalent in natures which are formed by the sharing of electrons.
- The acidic oxides of non-metals dissolve in water to form acids. The acidic oxides of non-metals turn blue litmus solution to red.
- Example: Carbon is a non-metal. When carbon burns in air it reacts with the oxygen of the air to form an acidic oxide called carbon dioxide: