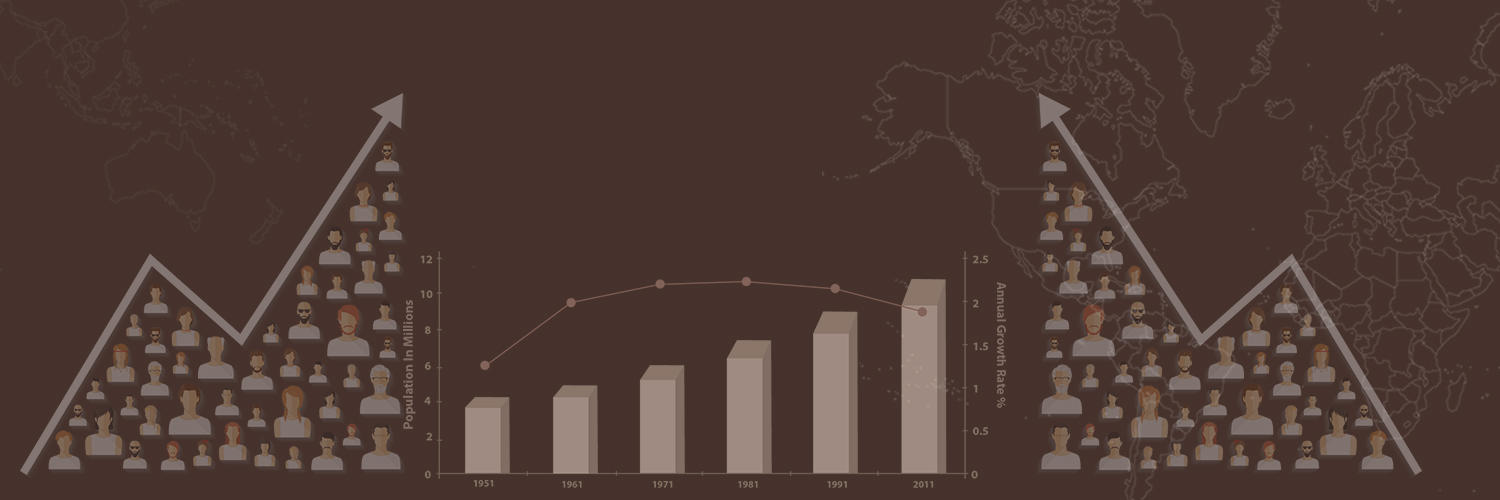
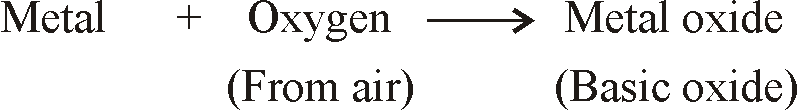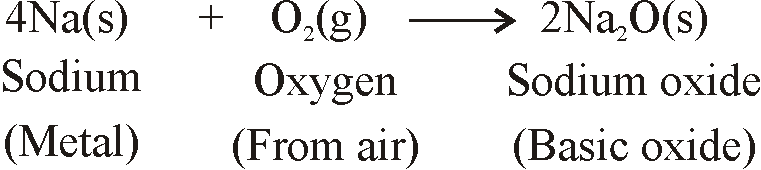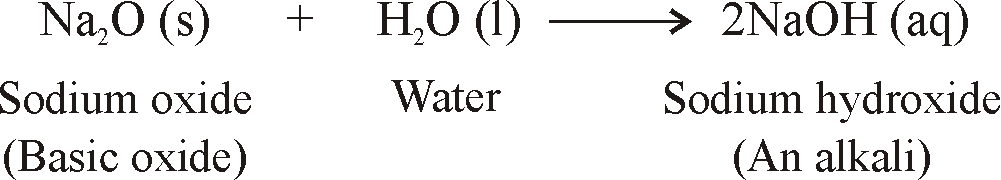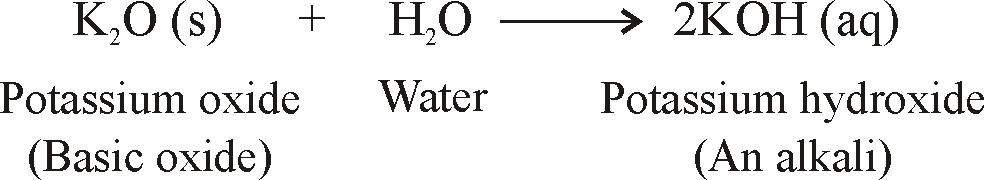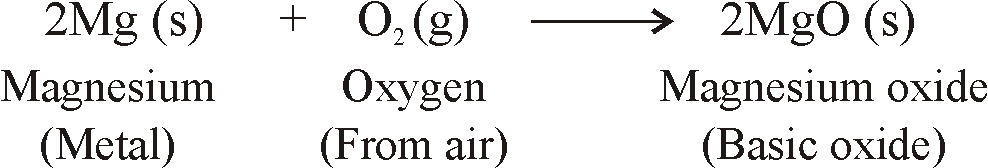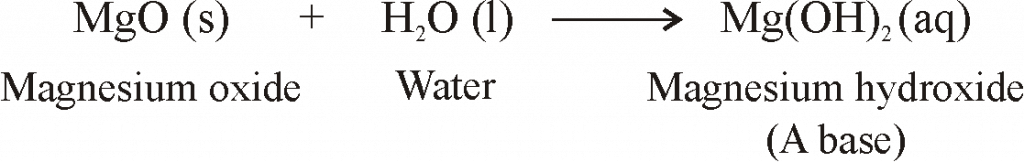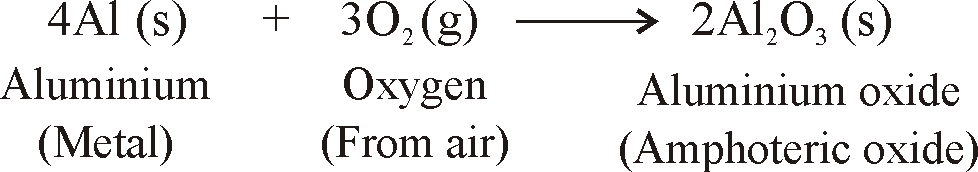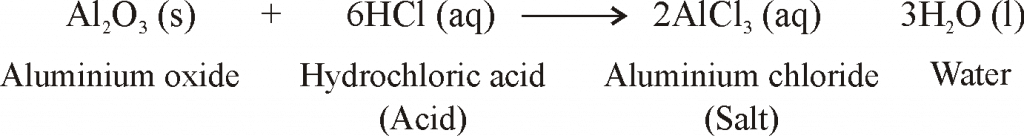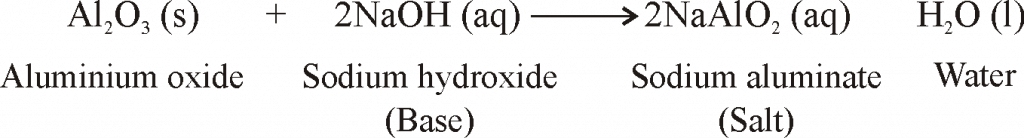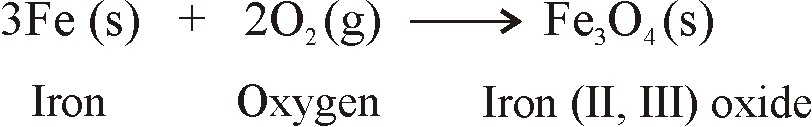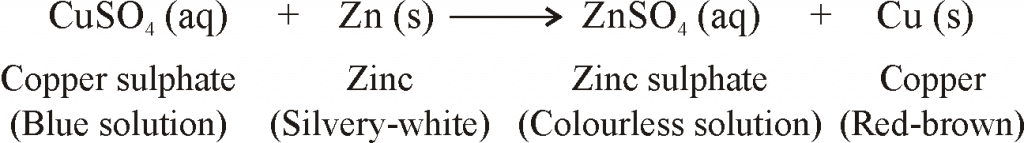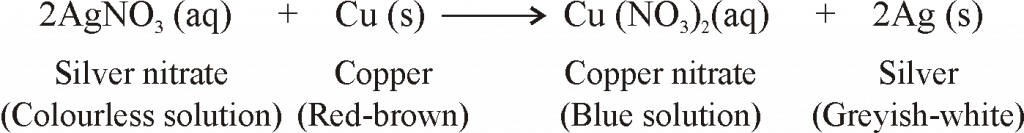REACTION OF METALS
REACTION OF METALS WITH OXYGEN (OF AIR)
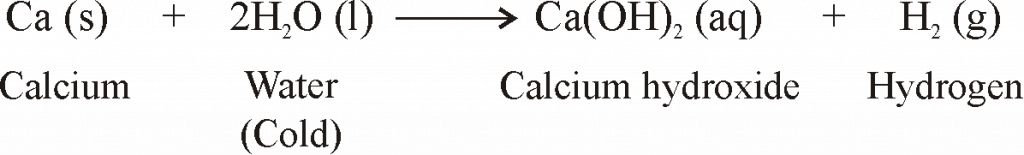
- When metals are burnt in air, Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides.
- However, if a strip of copper metal is placed in zinc sulphate solution, then no reaction occurs.
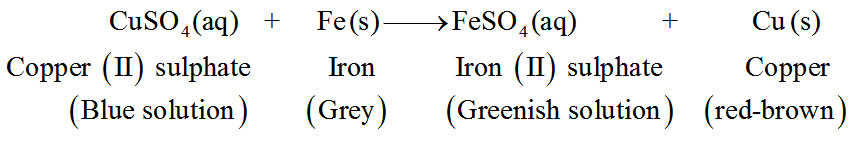
- Reaction of Iron with Copper, Sulphate Solution. When a strip of iron metal (or iron nail) is dipped in copper sulphate solution, then the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades gradually and red-brown metal is formed:
copper II sulphate Iron Iron II sulphate copper
(blue solution) (grey) (greenish solution) (red-brown)