
Acceleration of a body is defined as the rate of change of its velocity with time.
Acceleration can be represented as:
where v is the final and u is the initial velocity.
Objects moving around do not always do so at a constant speed, or in a constant direction. For example, planets revolving around the sun change their direction at every point, cars moving on a road subjected to traffic have different speeds at different point of time. Whenever we want a car to hurry up, we notice that its velocity increases. It is mathematically defined as rate of change of velocity.
Acceleration can also be interpreted from Newton’s second law which gives:
Where, is the net external force acting on the body,
a is acceleration and
m is the mass of the body.
So a body is accelerated only if net external force acts on the body and the acceleration produced in inversely proportional to mass.
Acceleration can be positive or negative depending on the direction of velocity.
When both act in the same direction then it is said as positive or the velocity of the body increases. For example, pressing the accelerator pedal of the vehicle increases the velocity.
Similarly when they act in opposite directions the acceleration is said to be negative or the velocity decreases. Example is, pressing the braking pedal of a vehicle so that the velocity decreases.
Acceleration can also be classified into two types:
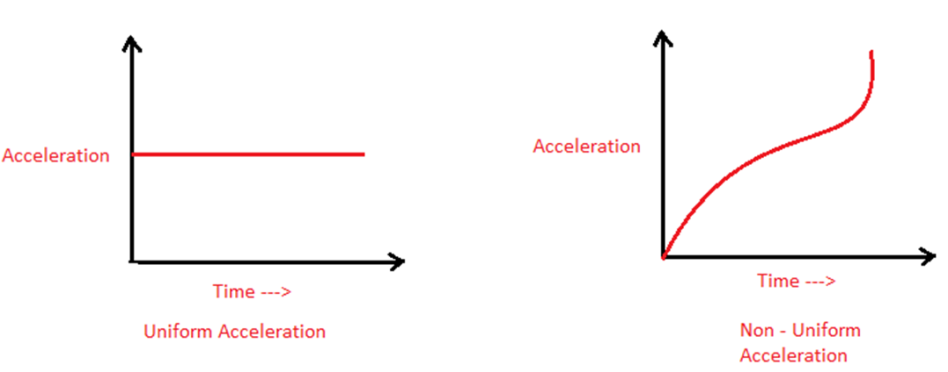
If the velocity of a body increases, the acceleration is positive, and if the velocity of a body decreases, the acceleration is negative.