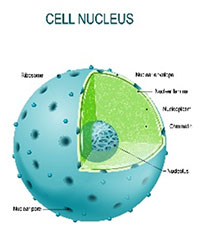
Properties:
Functions:
The following essential cellular processes take place in the nucleus:
Differences between nucleus and nucleoid:
| Nucleus | Nucleoid |
| Nucleus is larger in size. | Nucleoid is comparatively smaller in size. |
| It is covered by a double membrane envelope | A covering membrane is absent. It lies free in the cytoplasm. |
| Nucleolus is present in it. | Nucleolus is absent in it. |
| Its DNA content is equal to two or several DNA molecules. | Its DNA content is equal to a single DNA molecule. |
| Its DNA is associated with histone proteins to form chromatin. | In it histones are absent. DNA of a nucleoid is often naked. |