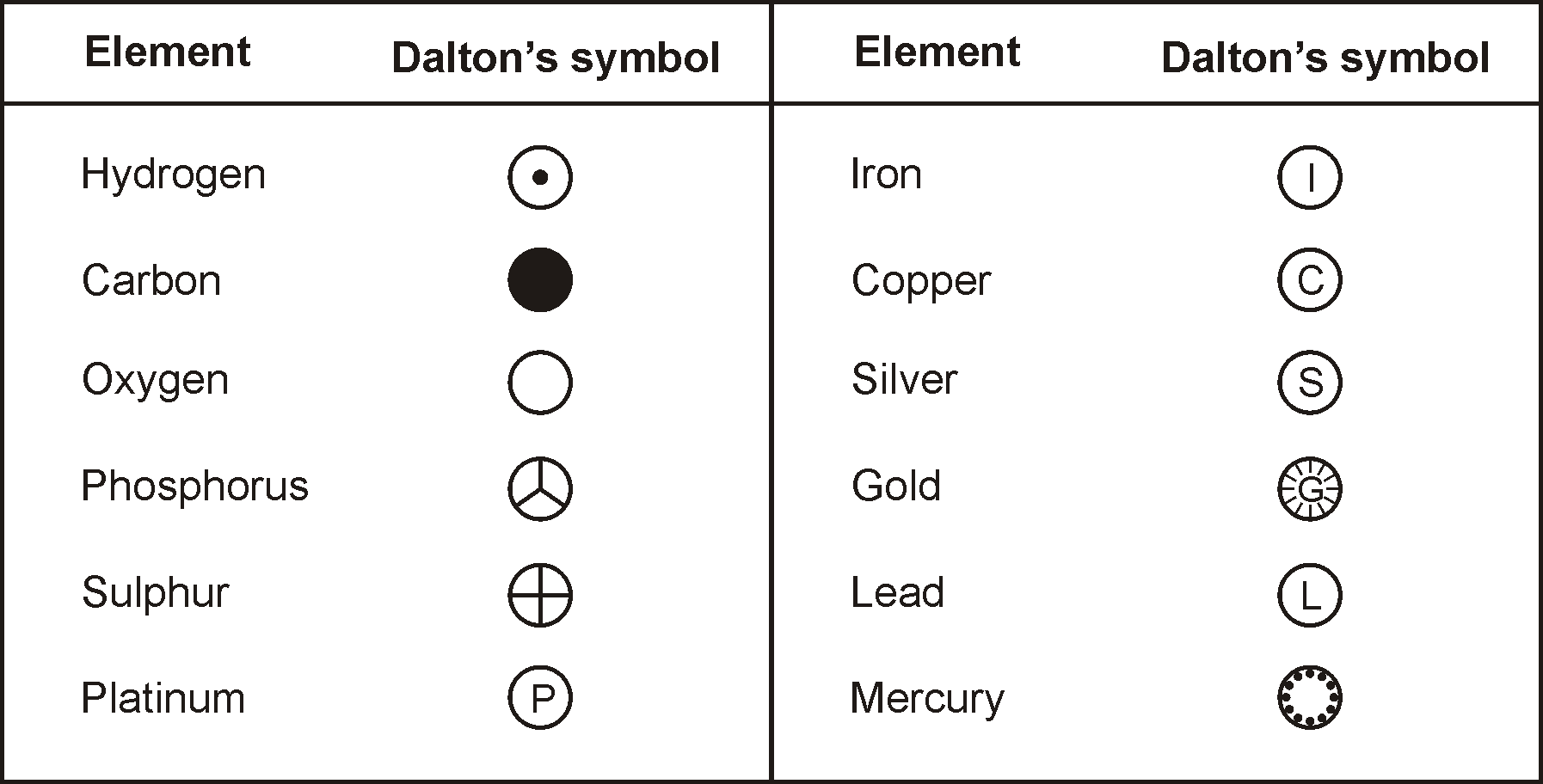
DALTON’S SYMBOLS OF ELEMENTS:
Symbols Derived from English Names of the Elements
| English name
of the element |
Symbol | English name
of the element |
Symbol |
| 1. Hydrogen | H | 14. Sulphur | S |
| 2. Helium | He | 15. Chlorine | Cl |
| 3. Lithium | Li | 16. Argon | Ar |
| 4. Boron | B | 17. Calcium | Ca |
| 5. Carbon | C | 18. Manganese | Mn |
| 6. Nitrogen | N | 19. Nickel | Ni |
| 7. Oxygen | O | 20. Zinc | Zn |
| 8. Fluorine | F | 21. Bromine | Br |
| 9. Neon | Ne | 22. Krypton | Kr |
| 10. Magnesium | Mg | 23. Iodine | I |
| 11. Aluminium | Al | 24. Barium | Ba |
| 12. Silicon | Si | 25. Cobalt | Co |
| 13. Phosphorous | P | 26. Uranium | U |
Symbols Derived from Latin Names of the Elements
| English name
of the element |
Symbol | Latin name of
The element |
| 1. Sodium | Na | Natrium |
| 2. Potassium | K | Kalium |
| 3. Iron | Fe | Ferrum |
| 4. Copper | Cu | Cuprum |
| 5. Silver | Ag | Argentum |
| 6. Gold | Au | Aurum |
| 7. Mercury | Hg | Hydragyrum |
| 8. Lead | Pb | Plumbum |
| 9. Tin | Sn | Stannum |
ATOMIC MASS OF AN ELEMENT
Or
Atomic masses of a few elements
|
Element |
Atomic mass (u) |
|
Hydrogen |
1 |
|
Carbon |
12 |
|
Nitrogen |
14 |
|
Oxygen |
16 |
|
Sodium |
23 |
|
Magnesium |
24 |
|
Sulphur |
32 |
|
Chlorine |
35.5 |
|
Calcium |
40 |
HOW DO ATOMS EXIST?
· Atoms of most of the elements are chemically very reactive and so they do not exist in Free State
H However, atoms of few elements called noble gases like helium, neon, argon and krypton, etc. are chemically unreactive and exists in the free state.