Structure:
Types of Connective Tissue:
In animals, there are following five types of connective tissues:
Blood:
Functions:
Bones:
Ligaments and Tendons:
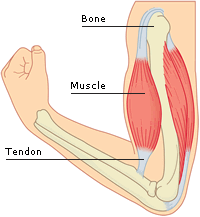
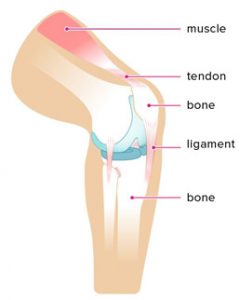
Differences between tendon and ligament
| Tendons | Ligaments |
| Inelastic. | Elastic. |
| Join muscles to bone. | Connect bones to bone. |
| Made up of white fibres. | Made up of white as well as yellow fibres. |
Cartilage
Areolar or Loose Connective Tissue
Functions:
Adipose Tissue
Functions: