
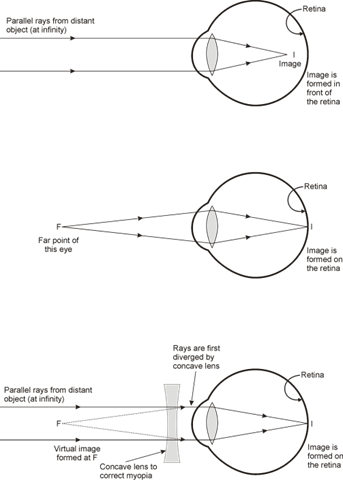
CAUSES OF MYOPIA:
It is caused due to:
SYMPTOMS OF MYOPIA:
HOW TO CORRECT MYOPIA?
Myopic eye do not diverge light rays coming from far off objects and hence a focused image cannot be formed on the retina. In fact, the rays converge much before they reach the retina. So, myopia is corrected by spectacles containing concave or diverging lenses of suitable focal length which will bring the image back on to the retina.
Focal length of the correcting lens = Distance of the far point from the eye.
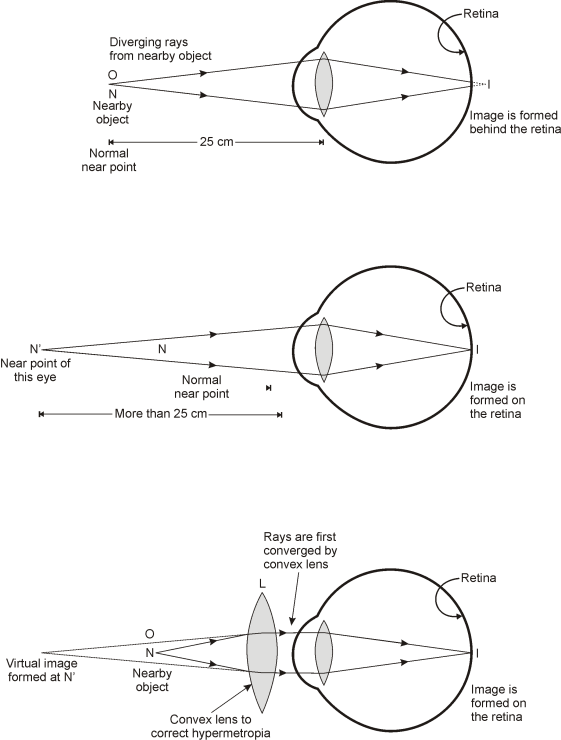
CAUSES OF HYPERMETROPIA:
It is caused due to:
HOW TO CORRECT HYPERMETROPIA?
Where y = Distance of the near point from the defective eye.
CAUSES OF PRESBYOPIA:
It is caused due to:
HOW TO CORRECT PRESBYOPIA?

Causes of Astigmatism
Types of Astigmatism
A person who cannot distinguish between various colours but can see well otherwise, is said to be colour-blind.
Causes of colour blindness
Colour blindness is caused due to lack of some cones in the retina of the eyes.