WORK
- Work is said to be done when a force acts on the body and the body moves in the direction of the force i.e. when a force produces motion.
- Work done in moving a body is equal to the product of force exerted on the body and the distance moved by the body in the direction of force.
- When a forceis applied to a block, it moves with some acceleration. This can be proved from Newton’s Second Law of Motion
Work done = Force x Distance
Substituting (2) in (1) we get:
- The speed of an object increases or decreases depending on the direction of the force.
- Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed so the energy must be getting transformed into some other form. In this case that is termed as work done.
- The energy decreases when negative energy is done and increases when positive work is done.
RELATION BETWEEN KINETIC ENERGY AND WORK
Work done by (F) = Change in kinetic energy
Where u is the initial and v is the final velocity of the body
Using third equation of motion,
ILLUSTRATIONS OF NO WORK
EXAMPLE 1:
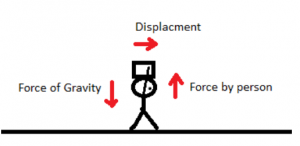
Consider the example of a boy carrying luggage. The force acting on the luggage is the force of gravity, which is vertical and displacement is horizontal. So the displacement in the direction of the force is zero, hence work done by gravity as well as the person is zero.
EXAMPLE 2:
When we push a wall, even though we feel fatigue but work done by on the wall is zero. This is because displacement of the wall is zero. So according to the formula,
W = F.s
W = F.0
W = 0
UNIT OF WORK
- The SI unit of work is newton metre, which is denoted as Nm or joule denoted as J.
- Work is a scalar quantity.
- One joule of work is said to be done, whenever a force of one newton displaces a body through a distance of 1 metre in its own direction
or
WORK DONE AGAINST GRAVITY
Work done in lifting a body = Weight of a body x Vertical distance
MEASUREMENT OF WORK
- When a force F acts along the direction of motion of the body,
Work done = Force x Distance
or
.
- When force F makes an angle 0 with the displacement s of the body,
- Work done on an object by a force would be zero if the displacement of the object is zero.
POSITIVE, NEGATIVE AND ZERO WORK
The work done by a force can be positive, negative or zero.
- Work done is positive when a force acts in the direction of the displacement.
- Work done is negative when a force acts opposite to the direction of the displacement.
- Work done is zero when a force acts at right angles to the direction of the displacement.