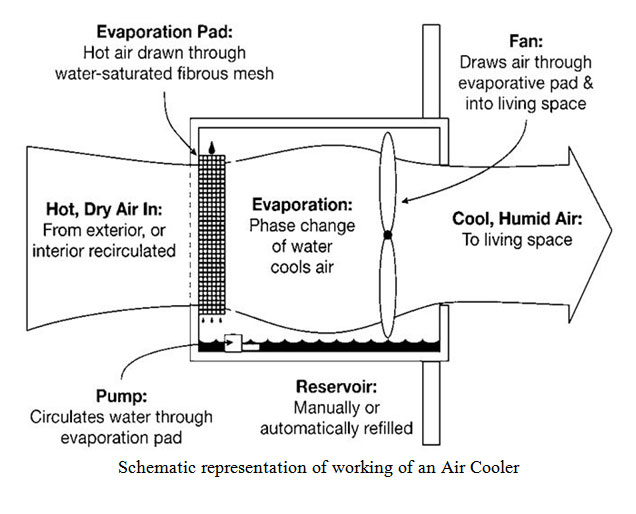
Factors Affecting Evaporation:
There are four factors which affect evaporation.
- Temperature: The rate of evaporation increases on increasing the temperature of the liquid.
- Surface Area of the Liquid: If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation increases.
- Humidity of Air: Humidity is the amount of vapour present in the air. When the humidity of air is low, then the rate of evaporation is high, and water evaporates more readily.
- Wind Speed: With the increase in wind speed, the particles of water vapour move away with the wind.
Cooling Caused by Evaporation:
- The process of evaporation that is accompanied by natural cooling is based on the principle that in order to change its state, matter must either gain or lose energy.
- If change of phase takes place from liquid to gas, molecules of matter require energy to overcome their potential energy by their kinetic energy.
- The liquid takes this energy from its surroundings.
- During energy transfer in most cases, an increase or decrease in temperature of the substance takes place, depending on whether the energy is being transferred from the substance to the surroundings or vice versa.
- Phase change does not result in observable heat transfer even though there is an increase in temperature of the substance till the boiling point is attained during evaporation.
- The molecules of the substance absorb heat energy continuously from the surroundings and thus cool the surroundings till they reach the boiling point.
- Thereafter they begin to break free from the liquid and turn into vapour.
- Since there is no change in temperature till the evaporation process is complete i.e. the entire liquid gets converted into vapour, the amount of energy required for this phase change is called the latent heat of vaporization, where the word ‘latent’ means ‘hidden’, meaning this heat will not change the temperature reading on a thermometer.