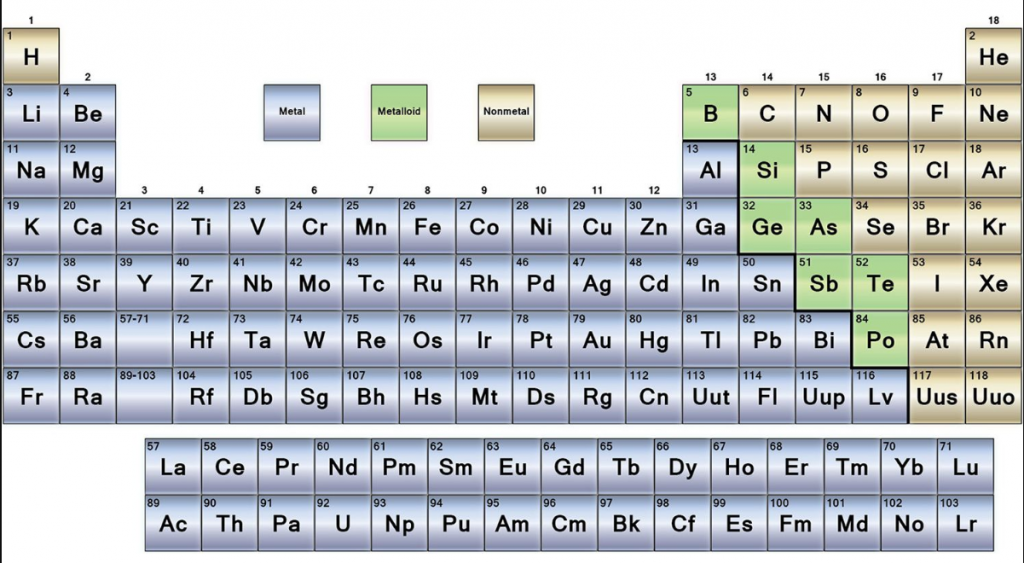
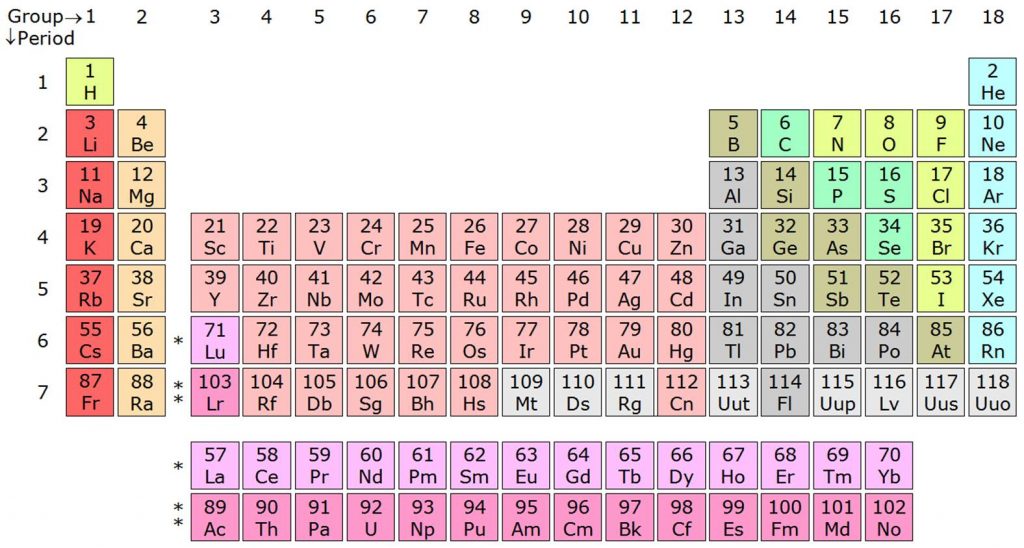
| Group number | Group name | Property |
| Group 1 or IA | Alkali metals | They form strong alkalis with water |
| Group 2 or IIA | Alkaline earth metals | They also form alkalis but weaker than group 1 elements |
| Group 13 or IIIA | Boron family | Boron is the first member of this family |
| Group 14 or IVA | Carbon family | Carbon is the first member of this property |
| Group 15 or VA | Nitrogen family | This group has non-metals and metalloids |
| Group 16 or VIA | Oxygen family | They are also known as chalcogens |
| Group 17 or VIIA | Halogen family | The elements of this group form salts. |
| Group 18 | Zero group | They are noble gases and under normal conditions they are inert. |