The process of reproduction is necessary for preservation and increases in population of a species. If the organisms would not reproduce the species to which they belong would extinct once they are dead. In order to maintain the species, an organism reproduces. Reproduction process is not necessary for an individual to live but necessary for perpetuation of its species.
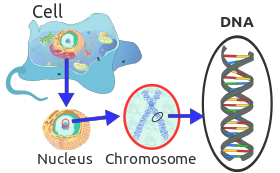
DNA found in chromosomes in the nucleus of the cells has the information about protein creation. This lead to body design of an organism. If the organisms are to make exact copies of them, the DNA should replicate to make an exact copy of it. DNA replicates in the cell with the help of various enzymes and this is accompanied by division of the basic unit of every organism i.e., the cell.
During replication (reproduction) each cell divides into two daughter cells having similar component of chromosomes as in the parent cell. This cell division is known as mitosis.
The process of replication is not completely reliable and some changes occur during the time of DNA replication. A new DNA is created which is different from the original one. Such a change in the information on DNA implies the initiation of variation. Different proteins lead to variation in the organism. This variation might be drastic or slow. The body designs that an organism inherited from its parent will not be considered anymore. Altered DNA copy will code for the proteins different from the original one. DNA copying depends upon the extent of similarity of the daughter cell with the parent cell. Any inaccuracy during DNA replication results in the daughter cell being different from the parent cell.
Variation exists in each time of DNA copying, as no biochemical reaction is absolutely reliable. Thus with each generation, daughter cells are subtly different from parent cells. This leads to variation in the species which is the basis of evolution.
Variation is limited in an asexually reproducing organism. Organisms create clones which are exact copies of themselves. But the chances of variation are very high in a sexually reproducing organism. One or more new offspring are produced from parent organisms through the process of reproduction. But, there is always a chance of variation and it is useful for the survival of species over time.
Living organisms increase their population and feed on available resources in their niche through the ability to reproduce. But the environment is not consistent and changes with the change in different factors like climate, temperature, availability of resources, etc. Changes in DNA and body design may result in difficulty to sustain themselves in their habitat. If a particular species is too adamant to change during environmental changes, it can’t survive in that habitat. Variations in species help them to adapt themselves to that particular environment and give them a chance of survival.
For example, bacteria living in water would perish if the water temperature is increased. However, thermophilic bacteria are the variants of bacteria which have become suited to higher water temperature. So, these may survive and thrive.